Hydrogen Sulfide (H2S) Detection
Portable & fixed-point H2S detectors for healthcare, pharmaceuticals, chemical manufacturing, agriculture, and environmental testing.
About Hydrogen Sulfide Detection
Hydrogen sulfide (aka dihydrogen monosulfide; sewer gas; stink damp; sulfur dihydride; sulfureted hydrogen) is a colorless gas having a strong odor of rotten eggs.
The major use of the compound is in the production of elemental sulfur and sulfuric acid. Hydrogen sulfide is also employed in the production of thiorganic compounds; alkali metal sulfides; and to separate deuterium oxide (heavy water) from normal water. It is utilized in metallurgy; in extreme pressure lubricants and cutting oils; and as an agricultural disinfectant.
Ranges We Detect For Hydrogen Sulfide
Sensor Range
0 - 50.0 ppm
0 - 20.0 ppm
0 - 2000 ppb
0 - 1000 ppb
0 - 500 ppb
0 - 200 ppb
Measurement Specifics
- Maximum Overload100 ppm
- Resolution< 0.03 ppm
- Typical Baseline Range-0.1 ppm to 0.3 ppm
- Maximum Overload100 ppm
- Resolution< 0.03 ppm
- Typical Baseline Range-0.1 ppm to 0.3 ppm
- Maximum Overload20 ppm
- Resolution< 0.01 ppm
- Typical Baseline Range-0.1 ppm to 0.1 ppm
- Maximum Overload20 ppm
- Resolution< 0.01 ppm
- Typical Baseline Range-0.1 ppm to 0.1 ppm
- Maximum Overload20 ppm
- Resolution< 0.01 ppm
- Typical Baseline Range-0.1 ppm to 0.1 ppm
- Maximum Overload20 ppm
- Resolution< 0.01 ppm
- Typical Baseline Range-0.1 ppm to 0.1 ppm
Not sure what range you need?
We’re here to helpINDUSTRIES WE SERVE
Portable Gas Detection
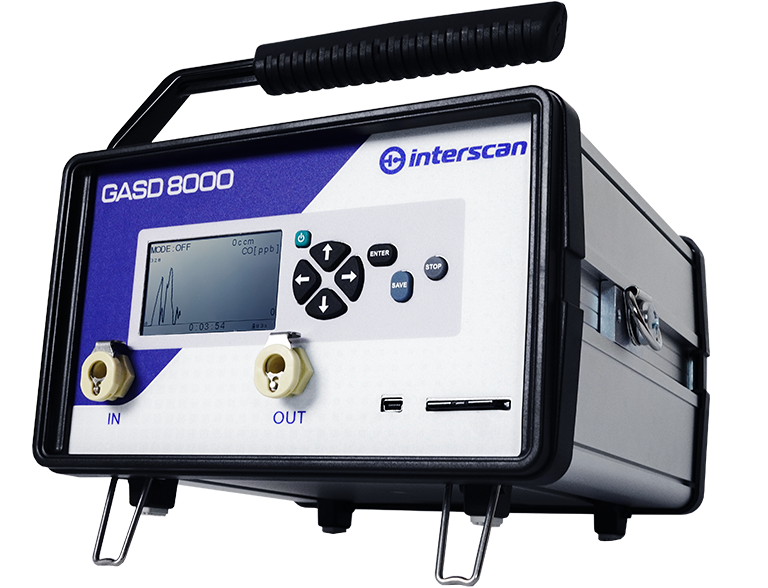
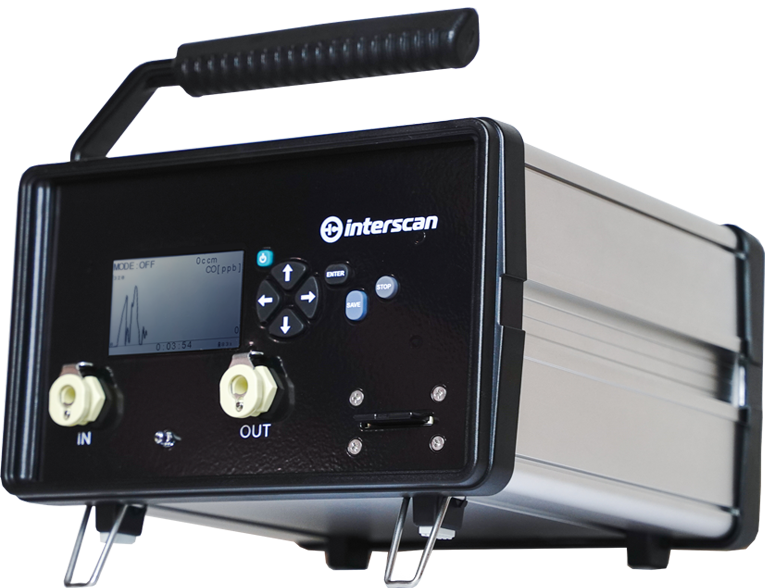
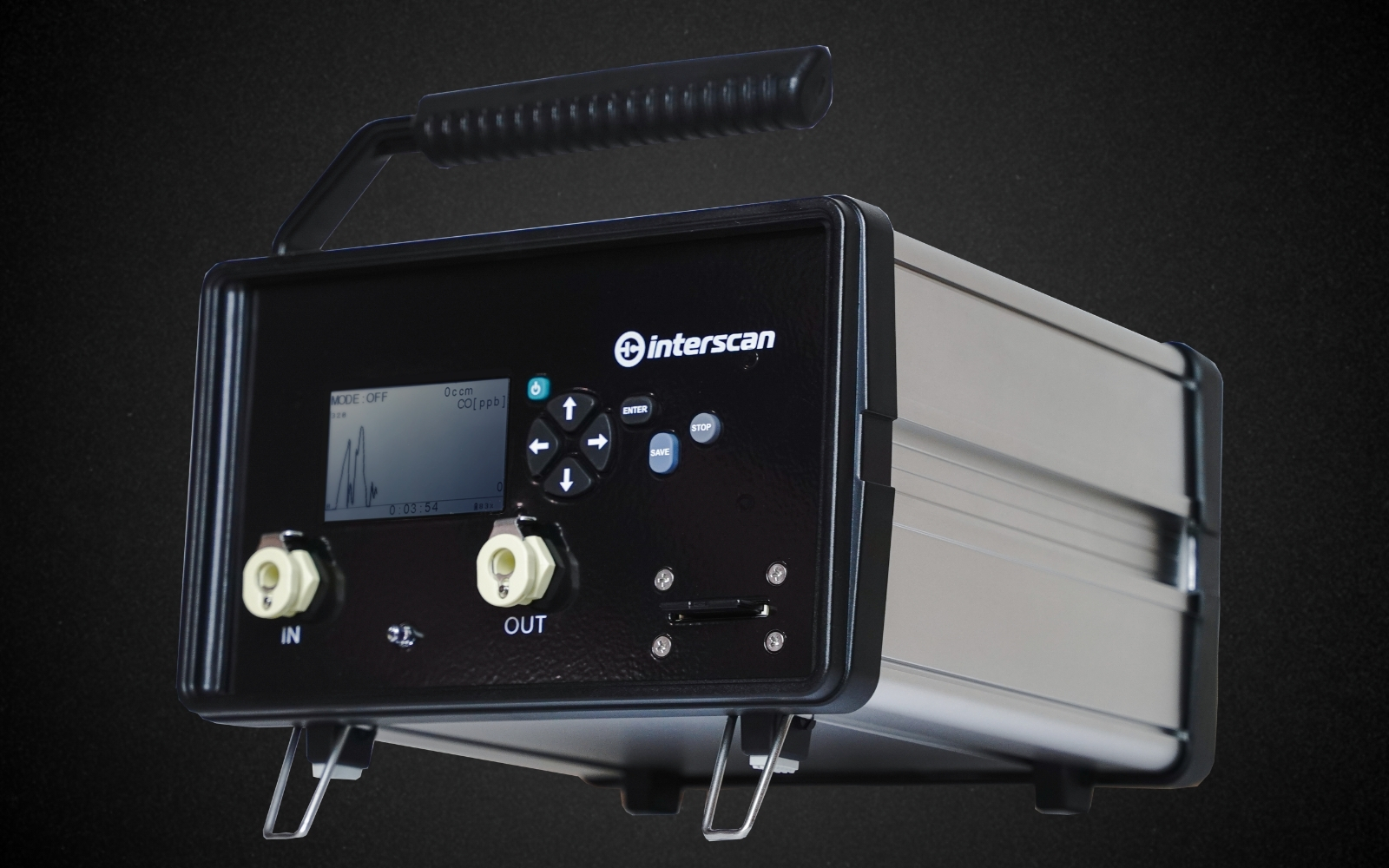
GASD 8000
Portable Gas Detector
Elevate Safety Standards with the GasD® 8000 Portable Gas Monitor Read more... about GASD 8000
Portable Gas Detection
GASD IS
Designed for Intrinsic Safety
Elevate Safety Standards with the GASD IS®: Purpose-Built for Explosive Atmospheres Read more... about GASD IS
Fixed Gas Detection
AccuSafe
Fixed Point Gas Detection
Precision Gas Detectors Tailored to Your Facility Read more... about AccuSafe